Browser Engine
Browser Engine
Built on Chromium, stripped of Google, hardened for privacy.
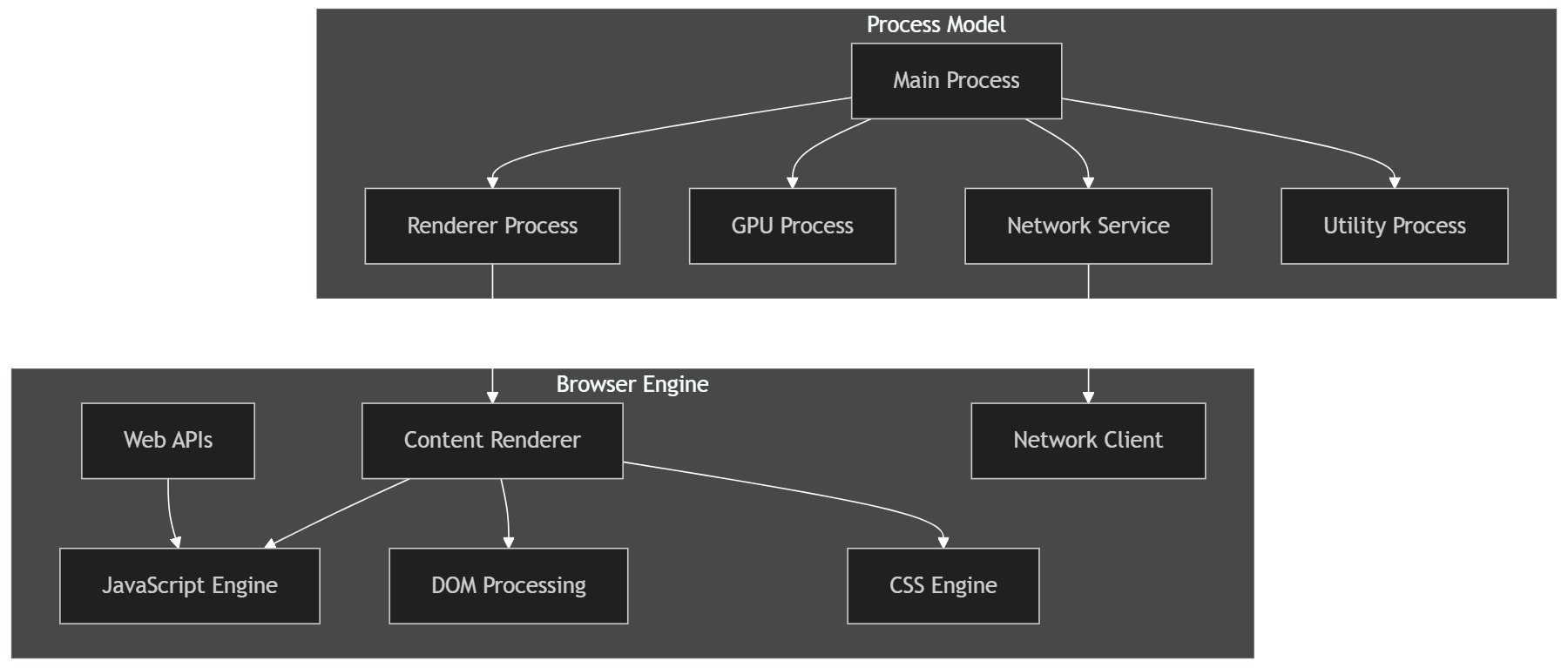
Base Technology
Chromium core
Blink rendering engine
V8 JavaScript engine
Latest stable branch
Electron framework
Cross-platform deployment
Native OS integration
Update system
DeGoogling Process
All Google services removed:
Removed components:
Google Safe Browsing
Chrome Web Store telemetry
Google account sync
Crash reporting to Google
Google DNS defaults
Background Google API calls
RLZ tracking
Google update mechanisms
Replaced with:
Privacy-respecting alternatives
Local crash handling
Custom update system
Privacy-first DNS providers
Privacy Patches
Custom patches applied to Chromium base:
Fingerprinting resistance
Canvas randomization
WebGL spoofing
User-agent rotation
Font enumeration blocking
Network privacy
WebRTC leak prevention
DNS query isolation
Referrer policy enforcement
Third-party cookie blocking
Tracking prevention
Tracker script blocking
Beacon interception
Pixel blocking
Redirect tracking prevention
Rendering Engine
Blink modifications:
Privacy-preserving rendering
Fingerprint randomization during canvas operations
WebGL context sanitization
Audio context fingerprint prevention
JavaScript Engine
V8 customizations:
Battery API blocking
Device API restrictions
Hardware enumeration limits
Timing attack mitigations
Extension System
Chromium extension API support:
Limited extension compatibility (privacy-vetted only)
Extension sandboxing
Permission review
Most features built natively to avoid extensions
Update System
Custom update mechanism:
No Google update services
Direct download from Macro servers
Signature verification
Delta updates for bandwidth efficiency
Performance Optimizations
Faster than standard Chromium:
No Google service overhead
Native ad/tracker blocking (loads fewer resources)
Optimized JavaScript execution
Reduced memory footprint
Platform Support
Windows:
Windows 10+ (64-bit)
Native Windows integration
Hardware acceleration support
macOS:
macOS 10.15+
Apple Silicon and Intel
Native macOS keychain integration
Linux:
Debian/Ubuntu-based distributions
AppImage and DEB packaging
Wayland and X11 support
Chromium performance. Privacy-first architecture.
Last updated